Pop Machina
POP-MACHINA aims to demonstrate the power and potential of the maker movement and collaborative production for the EU circular economy. We draw from a number of cut-edge technologies (factory-of-the-future, blockchain) and disciplines (urban planning, architecture) to provide the support necessary to overcome scaling issues; a typical drawback of collaborative production; to find the areas more in need of our intervention and to reconfigure unused spaces. We put forth an elaborate community engagement program to network, incentivize and stimulate through maker faires and events existing and new maker communities in all our municipalities. We build upon the current informal curriculum for maker skills development by nurturing the social side and we put educators and makers together to exchange ideas on the training modalities. A particular focus on the skill development of women and vulnerable groups will aim to empower these (underrepresented) segments to partake actively in collaborative production. In every pilot area we will demonstrate business oriented collaborative production of feasible and sustainable concepts from secondary raw material or other sustainable inputs, based on the needs and preferences of the local stakeholders. A thorough impact assessment framework with increased scope (e.g. social) will be co-designed with stakeholders after short basic assessment trainings and will be used in the assessment of our pilot work. Based on the findings we will kick-start a series of policy events to discuss openly – without pushing our results – the tax and legal barriers that hamper collaborative production.
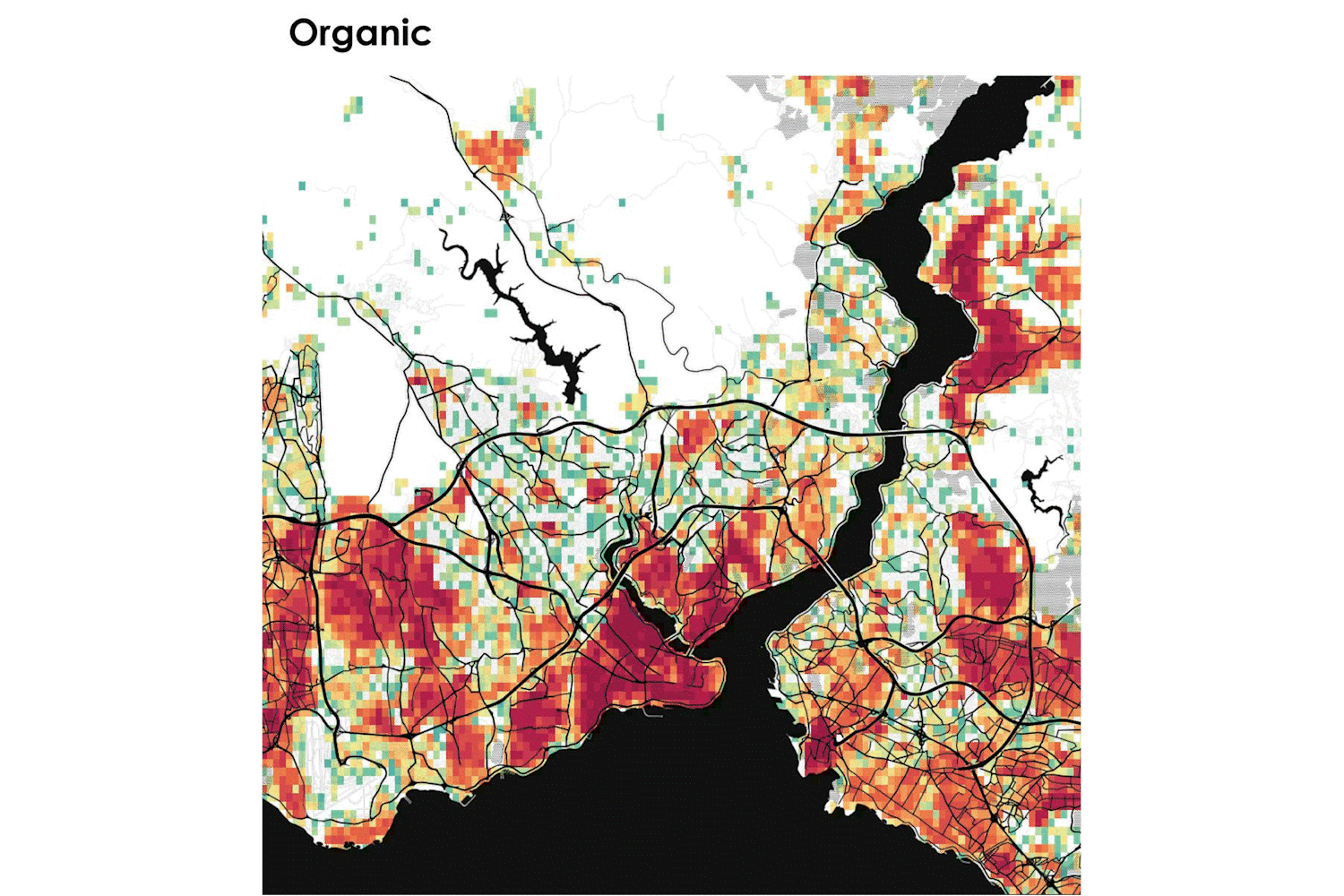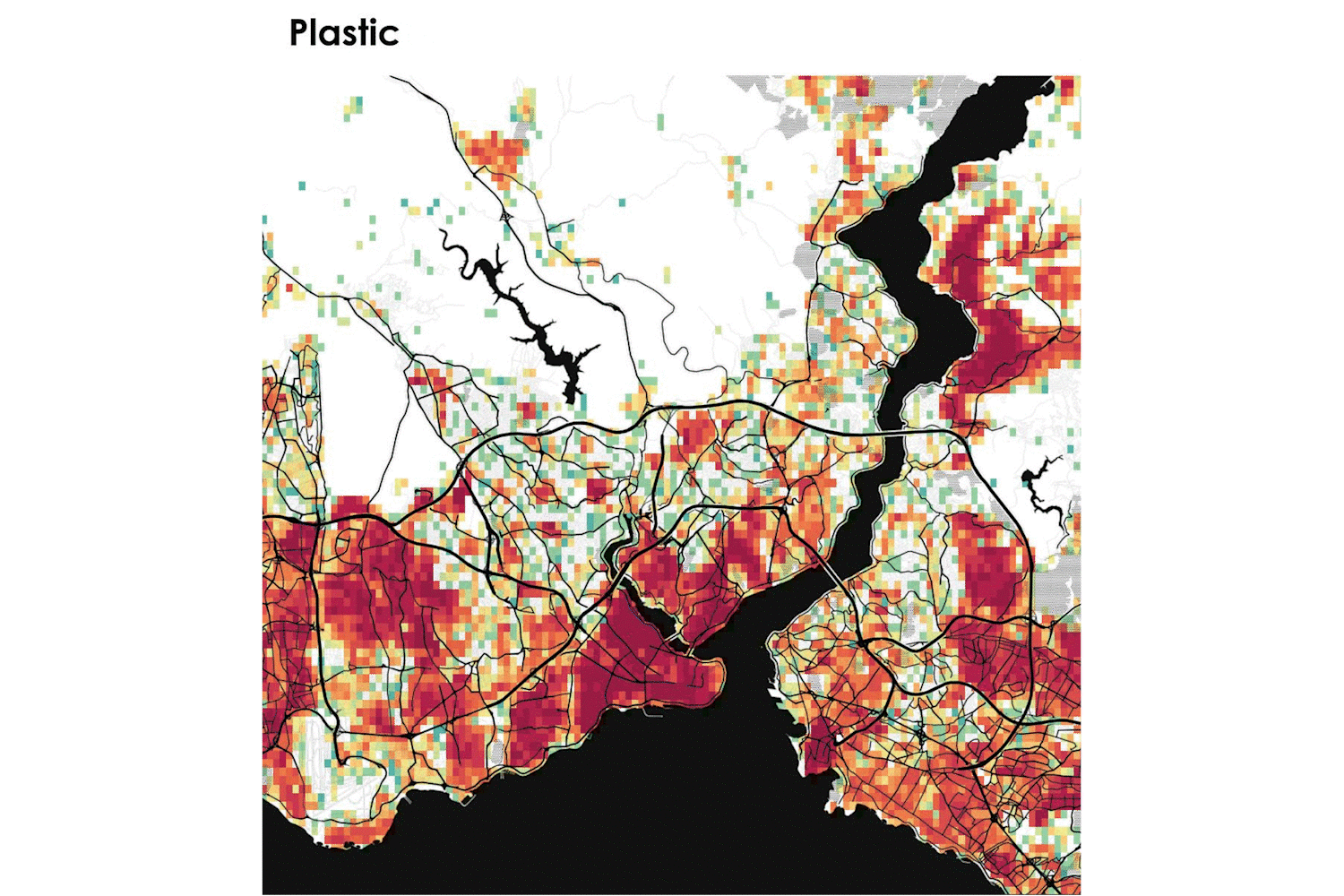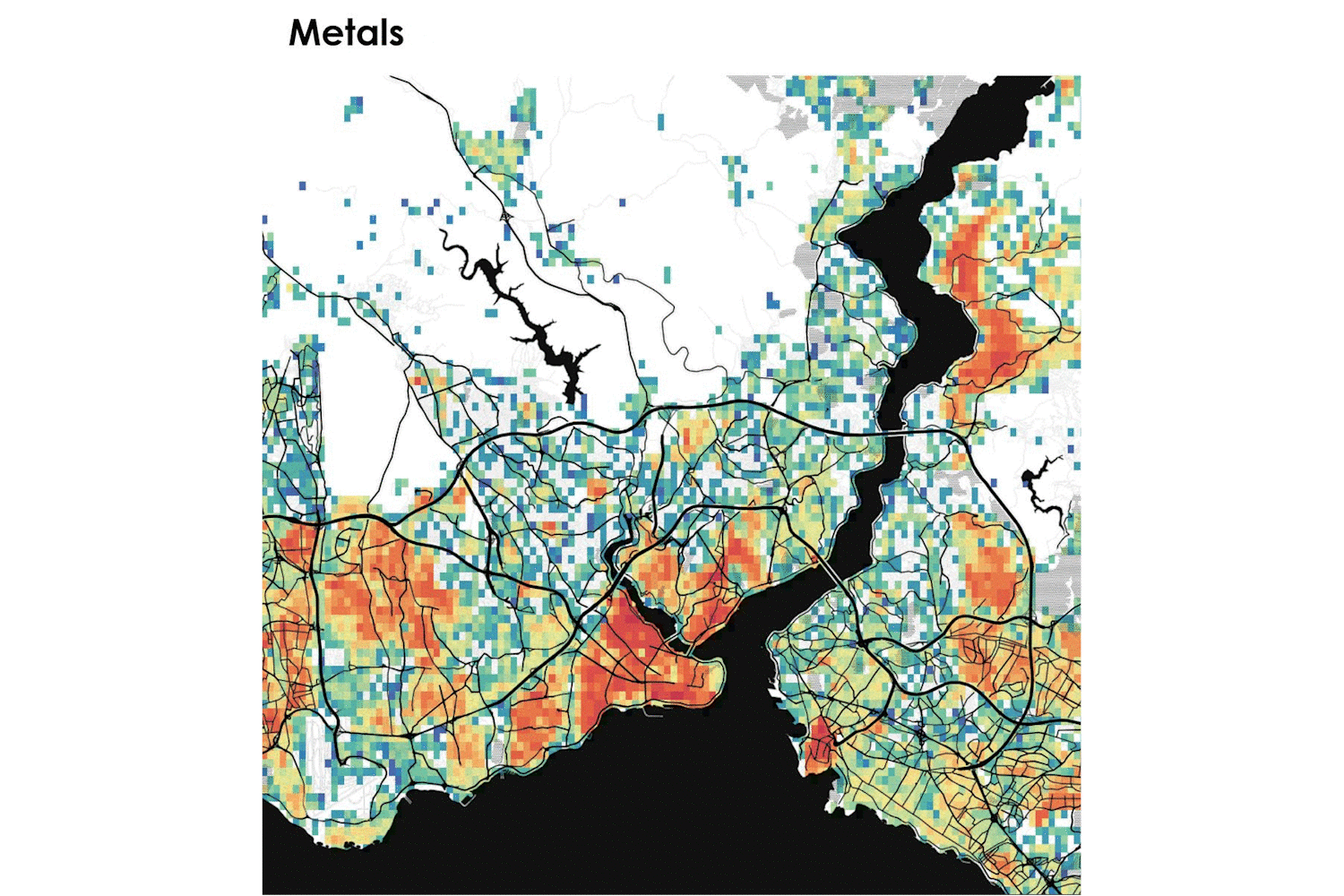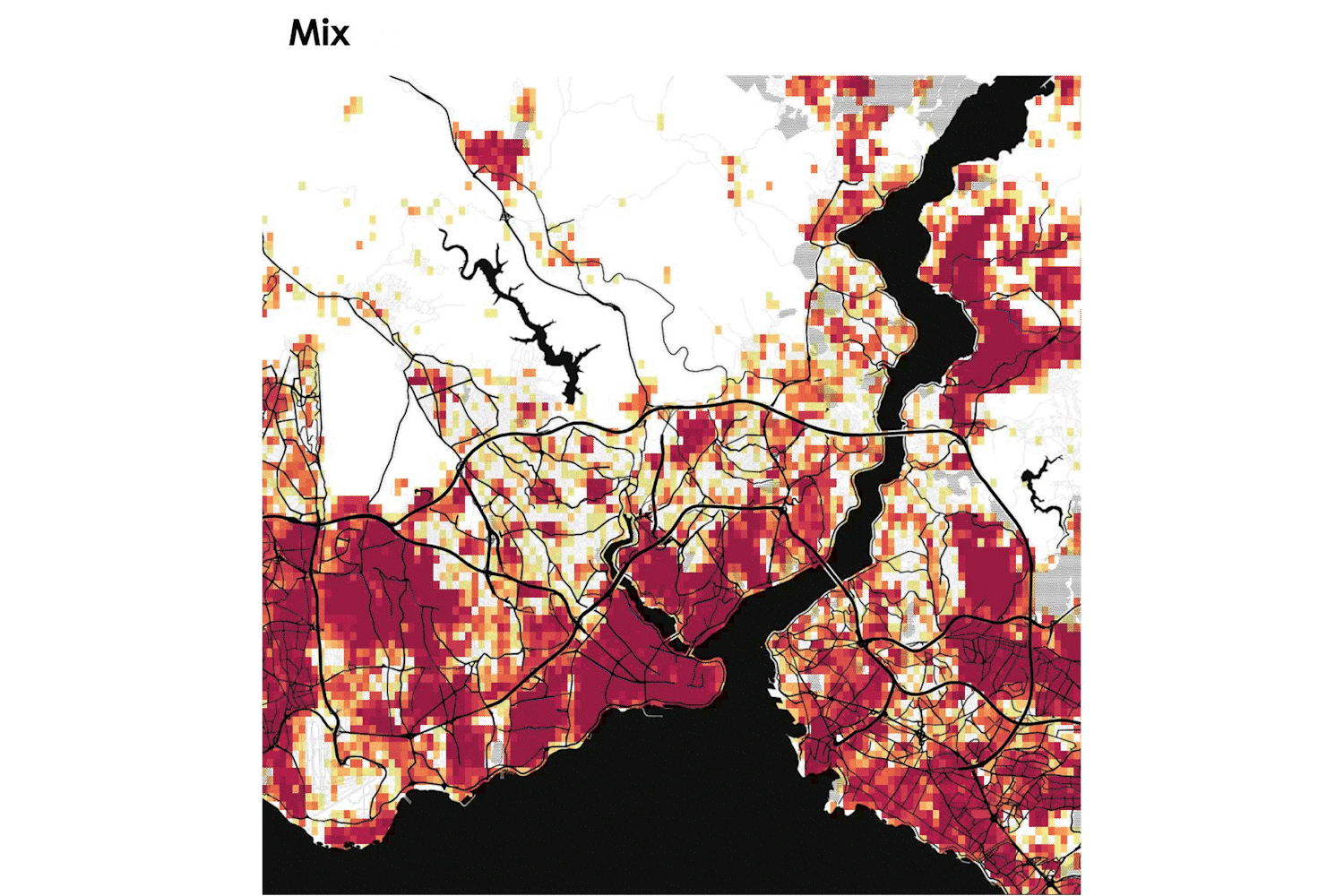
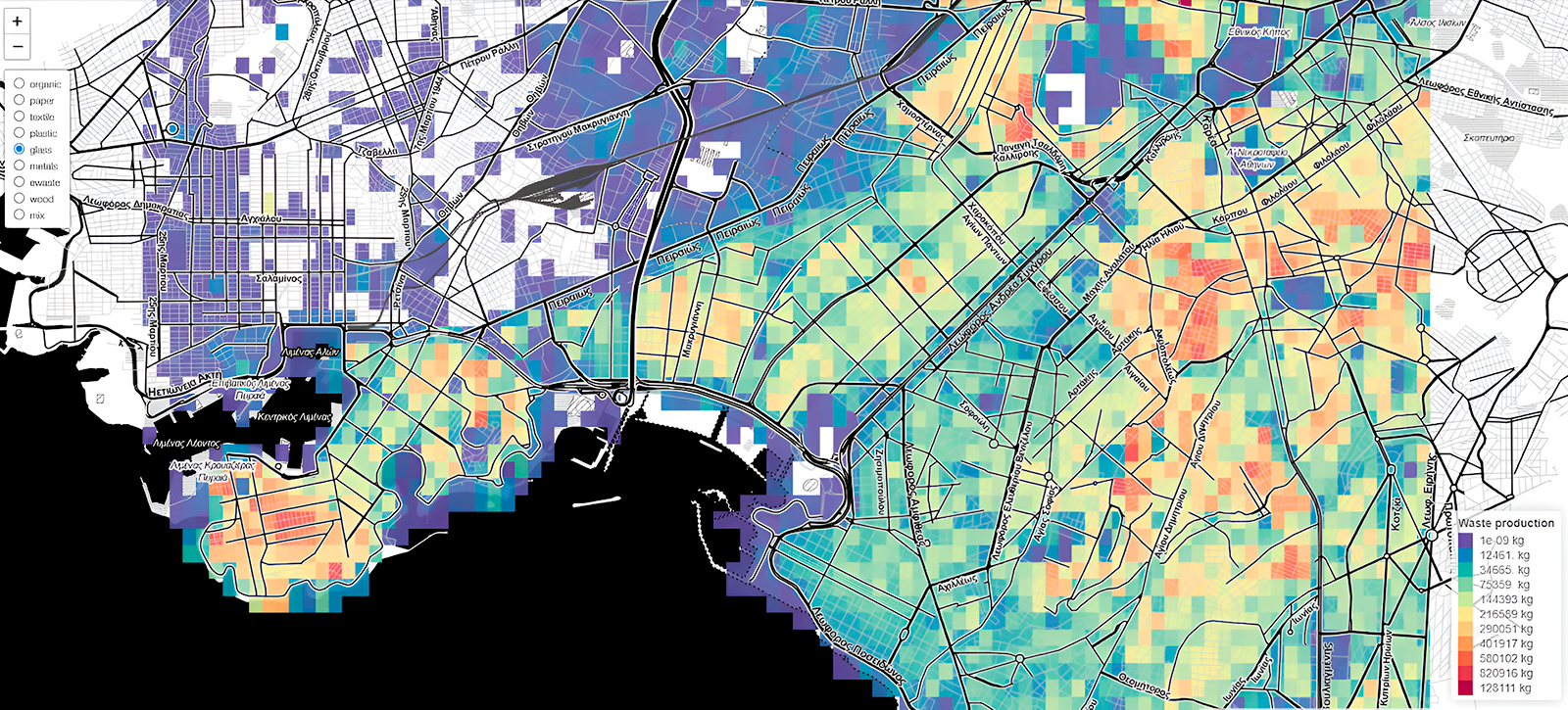
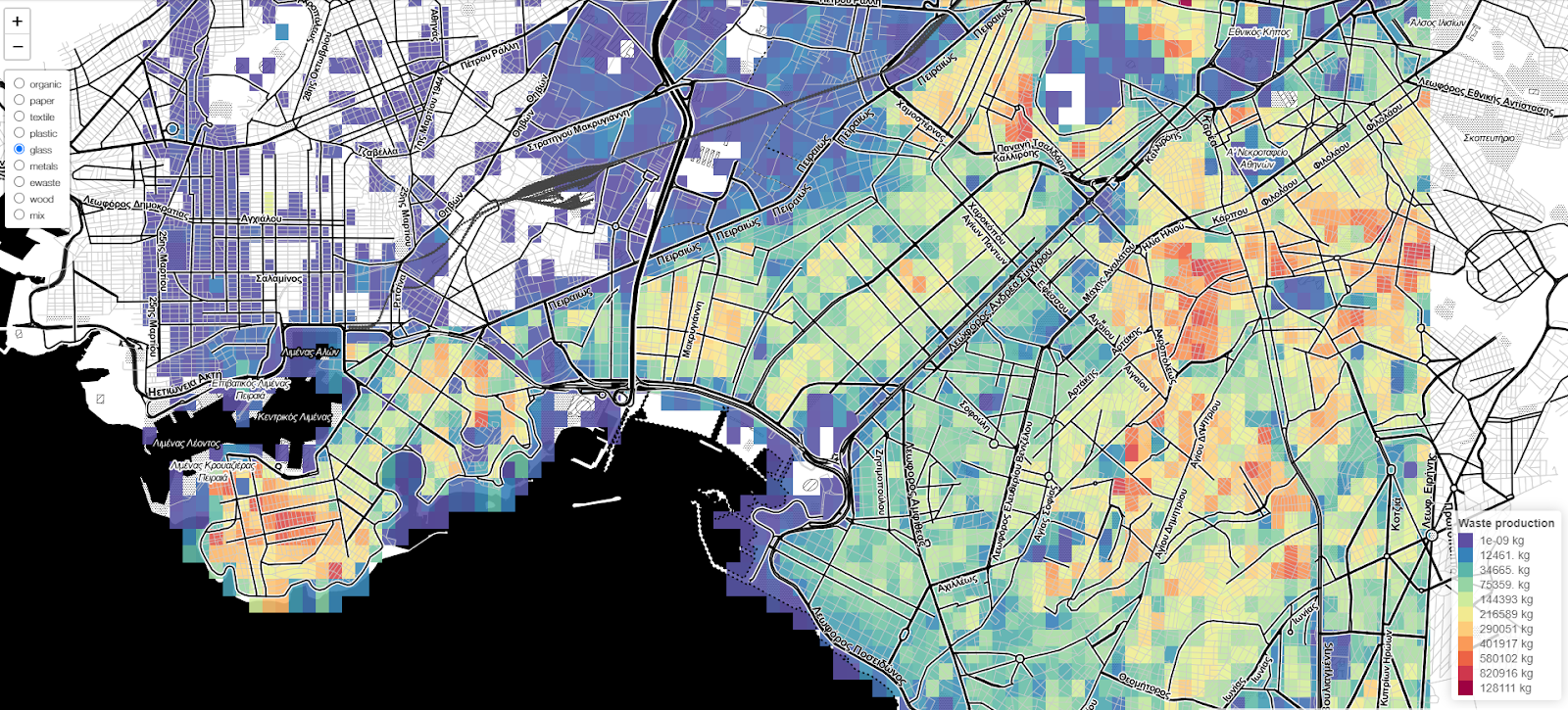
In the framework of the project, the AAG team developed a location-based visualisation tool for the estimation of municipal solid waste generation in the 7 pilot cities of Pop-Machina. The URBAN WASTE VISUALIZATION TOOL takes into consideration different typologies of waste and categories of activities (as waste generators) to understand the spatial distribution and density of waste generation to be considered as material resources for the maker spaces. The tool allows to address the following questions:
- Where is waste generated in the city?
- Who is responsible for the waste generation?
- How much waste is generated?
The maps shown in the tool provide maker spaces with useful information about materials that can potentially be reused or recycled as well as infrastructure planning for waste management to shape a new circular flow in the city.